Code-Memo
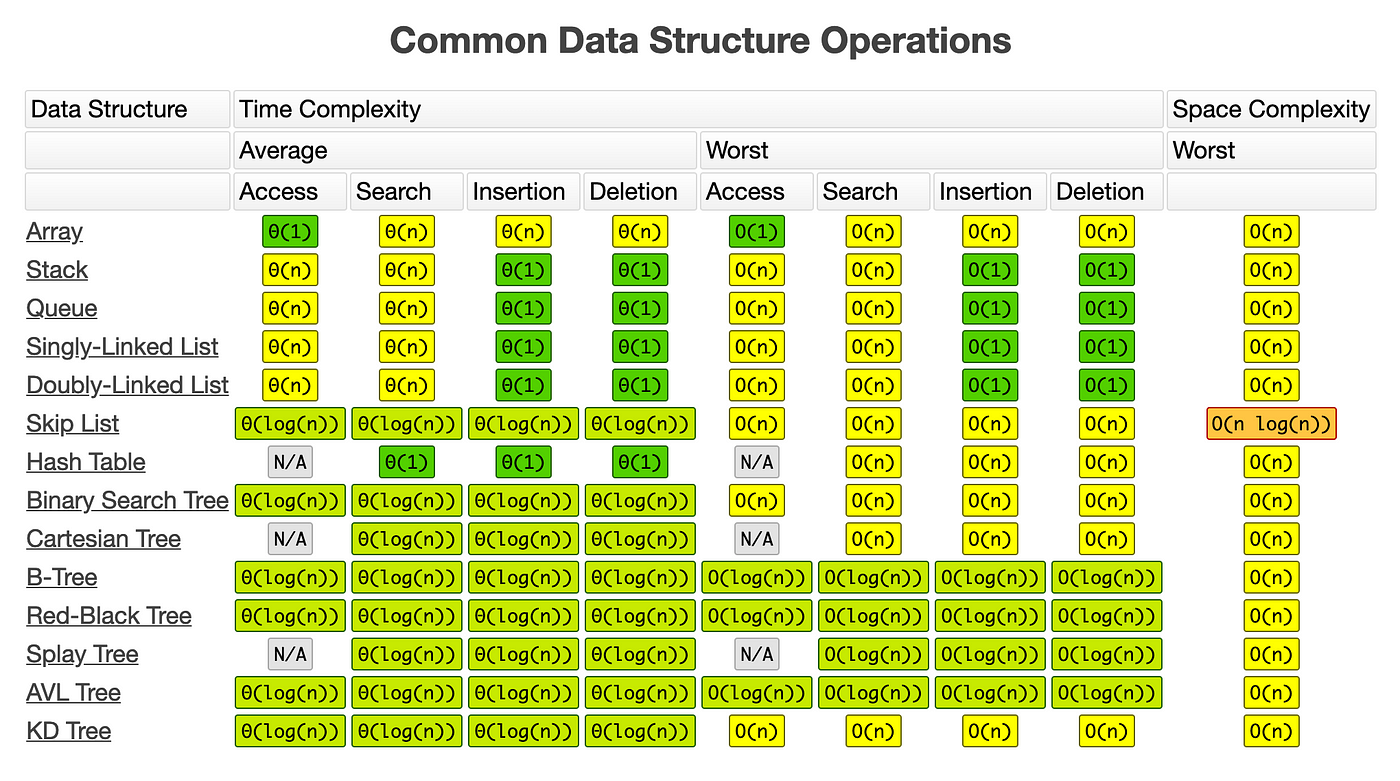
Data Structures
- Linear Data Structures
- Trees
- Hash Tables
- Graphs
- Heaps
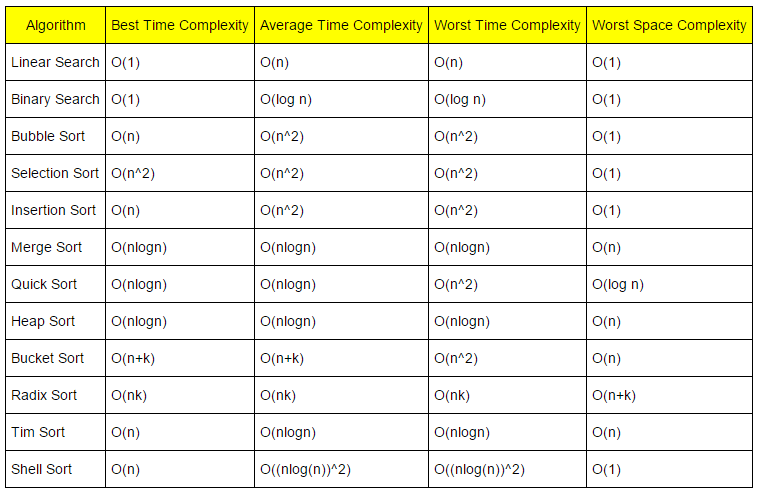
Algorithms
- Searching Algorithms
- Linear Search
- Binary Search
- Sorting Algorithms
- Bubble Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Selection Sort
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Counting Sort
- Radix Sort
- Heap Sort
- Recursion & Backtracking
- Factorial / Fibonacci
- Subset Generation
- Permutations / Combinations
- N-Queens
- Maze / Backtracking Pathfinding
- Palindrome Partitioning
- Dynamic Programming (DP)
- Memoization vs Tabulation
- 1D DP (Fibonacci, House Robber)
- 2D DP (Grid problems, Unique Paths)
- DP on Strings (Edit Distance, LCS, Palindromes)
- DP on Subsets / Knapsack
- Greedy Algorithms
- Activity Selection / Intervals
- Jump Game
- Minimum Platforms
- Graph Algorithms
- BFS (shortest path in unweighted)
- DFS (traversal, connected components)
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm (shortest path in weighted)
- Bellman-Ford (for negative weights)
- Floyd-Warshall (all pairs shortest path)
- Union-Find / Disjoint Set (cycle detection, Kruskal)
- Sliding Window / Two Pointers
- Fixed Window Size (max sum, average, etc.)
- Variable Window (min/max subarray length)
- Two Pointers for Sorted Arrays
LeetCode Problems
Some people focus on memorizing various algorithms, which can be beneficial at times but may also can be harmful to their problem-solving skills. Others rely only on problem-solving and might spend 10 hours on a single problem without finding a solution.
The most effective approach to solving coding problems combines both problem-solving skills and algorithm memorization. Instead of memorizing the exact code, you should be prepared to write any algorithm as needed. In other words, problem-solving is about recognizing patterns and knowing which algorithm to apply and implement.
Arrays and Hashing
- Contains Duplicate
- Contains Duplicate II
- Two Sum
- Two Sum II
- Maximum Subarray ⏳
- Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock ⏳
- Product of Array Except Self ⏳
- Group Anagrams
- Maximum Product Subarray ⏳
- Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array ⏳
- Search in Rotated Sorted Array ⏳
- Container With Most Water ⏳
Two Pointers
Stack
Sliding Window
Linked Lists
Binary Search
Trees
Tries
Time Complexity Graphs